
#Diagnosis code for atrial fibrillation code
ICD-10-CM codes would be I97.89 (other post-procedural complications and disorders of the circulatory system, not elsewhere classified) and I48.0 (paroxysmal atrial fibrillation) based on the instructional note to use an additional code to specify the disorder. You can measure your heart rate by checking your pulse in your wrist or neck.
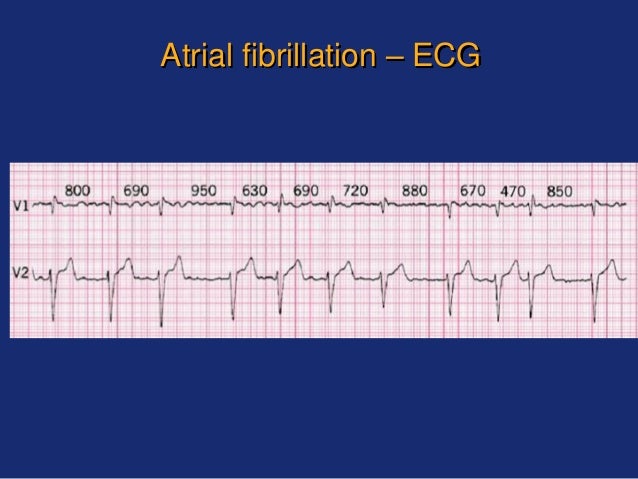
A normal heart rate should be regular and between 60 and 100 beats a minute when youre resting. The topic will review the use of echocardiography in evaluating patients with AF. Diagnosis Treatment Complications Atrial fibrillation is a heart condition that causes an irregular and often abnormally fast heart rate. Echocardiography plays a key role in evaluation and management of patients with AF. Now, let’s assume that the provider documented that the “post-operative course is complicated by paroxysmal atrial fibrillation requiring amiodarone drip.” This would code: Fibrillation > atrial > postoperative complication > paroxysmal. INTRODUCTION Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common treated arrhythmia. The ICD-10-CM code would be I48.0 (paroxysmal atrial fibrillation). This would code: Fibrillation> atrial > paroxysmal. Let’s assume documentation of post-operative paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. The physician has to specifically document that the post-operative atrial fibrillation is a complication of the procedure. ICD-9-CM coding allowed for post-operative atrial fibrillation to be coded as a complication, with supporting language in the Coding Clinic published for the fourth quarter of 2013. In these instances, the provider should be queried for clarification that the post-operative atrial fibrillation was, in fact, a complication. Some will agree that it is a complication, while others will say it is an expected outcome of the cardiac procedure. One area that varies among physicians is post-operative atrial fibrillation following cardiac surgery. On the other hand, if the post-operative atrial fibrillation required treatment, either with medications or defibrillation, this condition should be considered a complication. Next, if a patient develops atrial fibrillation post-operatively, what was the outcome? If the patient had several beats of atrial fibrillation noted on cardiac monitoring that resolved on its own without treatment, this should not be considered a complication. First, does the patient have a history of atrial fibrillation that is currently being treated? If so, then post-operative atrial fibrillation is not a complication of surgery and was present on admission. Determining whether or not to view post-operative atrial fibrillation as a complication has several defining factors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
